With survey design and methodology, comes various terminologies and jargons. These terms are important as they denote certain aspects of covering customer feedback or conducting marketing research. In this blog, we will discuss certain survey terminologies that will be easy to understand.
What is A Survey?
A survey is a technique for gathering information from a group of individuals, which can be done via different mediums such as messenger based surveys, web based chatbots, dynamic AMP email surveys or even via the good old pen and paper based surveys. Surveys aim to collect data on opinions, attitudes, and behaviors towards a specific topic, using various question types like multiple choice questions or open-ended questions.
A Short Guide to Survey Terminology
Surveys are an essential research tool in qualitative and quantitative research with a wide range of applications. There are various types of surveys that researchers can use depending on their research goals. Some commonly used types of surveys include market research surveys, customer satisfaction surveys, employee engagement surveys, political surveys, and event feedback surveys. Researchers can use these surveys as a reliable research tool for the entire research project.
Exploratory Surveys
Exploratory type of survey allows researchers to obtain data from a group of people without any preconceived notions about their responses. Less structured and more open-ended than other models like quantitative research studies, exploratory surveys assist in identifying potential problems or areas that require further exploration. Typically conducted through multi-modal methods such as phone interviews and online surveys or in-person focus groups, these types of studies are perfect for gaining insight into new markets before investing resources in larger statistical significance studies.
Descriptive Surveys
Descriptive surveys aim to collect detailed information about a specific target group’s demographics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions on specific topics and more. The sample size’s margin of error and confidence interval are essential factors in determining the center value or average value of respondents’ answers with statistical significance. The questions asked in descriptive surveys tend to focus primarily on closed-ended questions with rating scales but also incorporate open-ended questions for comments section feedback. Researchers may use various sampling techniques such as random sampling or targeted sampling based on specific criteria to ensure the survey reaches the ideal respondents without impacting completion rate. Field notes and interviewer training are important factors that determine data quality when conducting descriptive surveys.
Causal Surveys
Researchers use causal surveys primarily for research purposes in qualitative research. Causal surveys provide insight into factors responsible for specific outcomes or behaviors observed in a group of people. This makes the data useful in market research and other areas that require understanding consumer behavior or preferences. The results obtained from causal surveys help businesses and organizations make informed decisions. Causal surveys typically involve open-ended questions and rating scales as well as specific questions with pre-set responses.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling technique is a method where researchers collect data and analyze this data from a certain section of the population. This further gets divided into probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Under non-probability sampling, there are methods of random sampling, stratified sampling, convenience sampling, and snowball sampling. Researchers must carefully choose the appropriate technique to ensure that their survey results accurately represent the population they are studying. Researchers need also pay attention to response rates, drop-outs, completion rates and interviewer biases when designing surveys. Employing qualitative research methods like focus groups or multi-modal methods with quantitative research tools like online surveys can help counterbalance potential bias from sample selection or questionnaire design issues.
Questionnaire Types
A survey questionnaire may be crisp or have a certain length based on the goals, the marketer is willing to fulfill. Most commonly used customer feedback surveys have certain customer satisfaction metrics that are divided into closed-ended and open-ended questions. Dichotomous questionnaires are also commonly used in feedback forms and have only two possible answers: yes or no. This type of questionnaire is used for straightforward research purposes where there are limited options for responses available.
Most of the questions follow a certain structure, be it scale based, ranking type question and metric related survey. They are often closed-ended which also allows for open ended responses.
Customer feedback survey
Customer feedback surveys can be deployed in many ways. One can use the route of messenger based surveys using Whatsapp surveys or utilize the power of AMP interactive email questionnaires. Other methods include web based chat bots or in-application feedback collection facility.
As per this survey terminology, customer feedback forms aim to capture candid responses from people who have made a purchase or are in touch with an organisation. This form captures their experiences, ratings and preferences and maps patterns at different touchpoints or during their journey as a customer in the brand ecosystem.
Additional Terminologies for the Brand Surveyor
Apart from customer feedback surveys, brand surveyors may also use various other terminologies to conduct research and gather insights. Some of these include:
Margin of error
The margin of error is a statistical measure that helps to determine the accuracy of a survey’s results. It refers to the range in which the true value of a population parameter may lie based on the sample data collected. The margin of error is usually expressed as a percentage or a number of points.
Scale
In a sampling term, scale refers to the process of adjusting survey responses or measurements to a different numerical range. Scaling helps transform raw data into a standardized format, allowing for meaningful comparison and analysis.
Sampling error
Sampling error is the difference between the characteristics of a sample and the characteristics of the population being studied. It occurs due to the fact that it is not feasible to survey every single member of a population, so researchers rely on sampling to gather representative data. The larger the sample size, the smaller the sampling error will be.
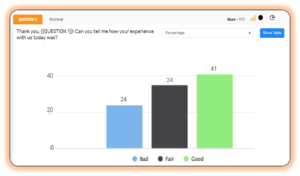
Response rate
Response rate refers to the number of people who respond to a survey compared to the total number of people who were invited or eligible to respond. A low response rate can affect the validity and reliability of survey results as it may introduce bias into the data.
Customer Satisfaction Metrics
This includes the most common terms of net promoter score or NPS, CSAT score or the customer satisfaction score and the CES score or the customer effort score. These are some of the most used and standardized methods of collecting feedback from the target audience. These metrics can be launched as Whatsapp surveys, AMP email forms or via in-app feedback form. These metrics fall under the closed-ended question with a space for open-ended responses.
Closed-ended and open-ended questions
Closed ended questions follow a certain framework of question. It comes with predefined metrics of measurements, scales and questionnaire. It allows respondents to answer as per the given option. There are multiple standardized methods of collecting marketing research or customer feedback in a survey.
Open-ended questions seek to collect candid, expressive and open responses from the people. For open ended forms, people are free to share their thoughts, experiences, complaints or testimonials. Messenger based survey empowers brands to collect multimedia responses in the form of audio, video, or photos. All collectively bring rich data to the dashboard.
Conclusion
In research, survey terminology plays a critical role in ensuring accuracy and consistency of results. Sampling error can be minimized by increasing the sample size, while response rate is essential for reliable data. Closed-ended questions are useful for collecting structured data, while open-ended questions provide rich, candid feedback. Understanding these survey terminologies can help researchers collect and analyze data with greater precision and clarity.
Merren offers a robust customer feedback tool that empowers every marketer to curate surveys and collect actionable data. Sign up for a 14 day free trial and supercharge your feedback collection activity.





